The United States is globally recognized as a leader in healthcare innovation, education, and clinical excellence. For students aspiring to advance their nursing careers, pursuing a Master’s in Nursing in the U.S. offers unparalleled opportunities for specialization, leadership roles, and career advancement. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment for advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs), including nurse practitioners (NPs), nurse anesthetists, and nurse midwives, is projected to grow by 38% between 2022 and 2032, much faster than the average for all occupations. Pursuing a Masters in Nursing in USA opens doors to advanced clinical roles, leadership opportunities, and some of the highest-paying healthcare jobs globally.
Key Highlights – Masters in Nursing in USA
- Top-Ranked Universities: Study at world-leading institutions like Johns Hopkins University, University of Pennsylvania, and Duke University, ranked among the top nursing schools worldwide.
- Duration: Programs typically last 1.5 to 2 years, with options for specializations like Nurse Practitioner, Clinical Leadership, or Public Health.
- Tuition Fees: Varies between $35,000 – $70,000 per year, depending on the university and program type.
- Career Scope: High-paying roles like Nurse Practitioner, Clinical Nurse Leader, and Nurse Educator await graduates—with starting salaries of $85,000 – $120,000+ per year.
- Future Demand: With the U.S. nursing workforce expected to grow by 40% by 2031, demand for advanced practice nurses is at an all-time high.
- Types of MSN Courses: Choose from MSN (General), Direct-Entry MSN, or Nurse Practitioner tracks like Family Nurse Practitioner (FNP), Psychiatric NP, and more.
Types of Master’s Nursing Programs Available in the USA

The scope of a Masters in Nursing in USA extends far beyond hospitals; graduates are shaping healthcare policy, research, and patient advocacy worldwide. The U.S. offers a wide variety of Master’s-level nursing programs to meet the diverse career goals and educational backgrounds of students. Whether you’re an experienced registered nurse (RN) looking to advance in clinical practice or someone from a non-nursing background aiming to transition into the field, there’s likely a tailored program for your needs.
1. Master of Science in Nursing (MSN)
The MSN is the most common and widely recognized Master’s degree in the field of nursing in the U.S. It focuses on clinical practice, research, leadership, and specialization. Most MSN programs allow students to choose a concentration such as:
- Family Nurse Practitioner (FNP)
- Adult-Gerontology Nurse Practitioner
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (PMHNP)
- Pediatric Nurse Practitioner
- Clinical Nurse Leader (CNL)
- Nurse Educator
- Nurse Administrator
This program is ideal for registered nurses who already hold a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) and want to deepen their expertise or shift into specialized clinical roles.
Duration: 18 to 36 months
Eligibility: BSN, RN license (some direct-entry options available)
2. Master of Nursing (MN or MSN-Entry) / Entry-Level Master’s in Nursing
This program is designed for individuals who do not have a nursing background but hold a bachelor’s degree in another field. Often referred to as Direct-Entry MSN or Entry-Level Master’s in Nursing, these programs are highly intensive and prepare students for licensure and advanced practice in a condensed timeline.
These programs combine pre-licensure nursing education with graduate-level coursework and clinical hours.
Duration: 2 to 3 years
Eligibility: Non-nursing bachelor’s degree, prerequisites (e.g., anatomy, physiology, statistics)
3. Clinical Nurse Leader (CNL) Program
A relatively newer role, the Clinical Nurse Leader is trained to improve patient outcomes through evidence-based practice and system management. This is an advanced generalist role (not a nurse practitioner) and is ideal for those who want to bridge direct patient care and leadership.
Duration: 2 years
Eligibility: BSN (or direct-entry variant), RN license
4. Online and Hybrid MSN Programs
Online MSN programs have gained significant popularity, especially for working professionals. These may be fully online or hybrid (online coursework with required in-person clinicals). Online programs may be available for:
- Nurse Educator
- Nurse Administrator
- Some NP specializations (clinical placements are local)
Many U.S. universities offer CCNE-accredited online MSN programs, making them accessible to both domestic and international students.
Top Providers: Johns Hopkins, Duke, University of South Carolina, Georgetown (online MSN)
5. MSN with Dual Degrees
Some universities offer MSN programs in conjunction with other degrees, such as:
- MSN/MPH (Public Health)
- MSN/MBA (Nursing Administration & Business)
- MSN/MPA (Public Administration)
These programs are ideal for those looking to move into healthcare policy, management, or administration.
6. Bridge Programs (RN to MSN)
For registered nurses without a BSN, RN-to-MSN programs offer a bridge directly from an associate degree to a master’s degree. These may take longer but are a good alternative for ADN-prepared RNs aiming for advanced practice roles.
Suggested Post: Masters in health informatics in USA
Admissions Requirements for Masters in Nursing in USA
Admission into a Master’s in Nursing (MSN) program in the U.S. is competitive, particularly at top-ranked universities and for specialized tracks such as Nurse Practitioner (NP) or Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA). While the exact requirements vary slightly across institutions and programs, the following are the standard eligibility criteria and required documents that most universities expect applicants to fulfill.
Academic Qualifications
- For Traditional MSN Programs:
- Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) from an accredited institution (typically CCNE or ACEN accredited).
- Minimum GPA requirement: Usually 3.0 or above on a 4.0 scale. Some schools may accept 2.75 with strong experience or references.
- For Direct-Entry/Entry-Level MSN Programs:
A non-nursing bachelor’s degree (e.g., B.A., B.Sc. in Psychology, Sociology, Biology, etc.).
Completion of prerequisite courses such as:
- Human Anatomy & Physiology
- Microbiology
- Statistics
- Developmental Psychology
- Nutrition
- Chemistry (sometimes required)
Prerequisites must be completed within 5–10 years prior to application, depending on the program.
RN License (If Applicable)
- For traditional MSN programs:
A current and valid Registered Nurse (RN) license from a U.S. state is required.
- For international applicants:
- May be required to pass NCLEX-RN after graduation if intending to practice in the U.S.
- Some programs offer pre-licensure MSN tracks where the RN licensure is obtained during the course of study.
Official Transcripts
- Applicants must submit official academic transcripts from all post-secondary institutions attended.
- Transcripts from outside the U.S. often need to be evaluated by a credential evaluation agency such as WES (World Education Services) or ECE.
English Language Proficiency (For International Students)
If your prior education was not in English, you’ll need to demonstrate English proficiency via one of the following tests:
| Test | Minimum Required Score |
| IELTS | 6.5 – 7.0 overall (no band < 6.0) |
| TOEFL iBT | 80 – 100 (depending on program) |
Some universities waive this requirement if the student has completed previous education in English-speaking countries or institutions.
GRE or MAT (Optional at Most Schools)
- Many top MSN programs have waived the GRE requirement.
- However, schools such as Yale, Duke, or Johns Hopkins may still consider GRE for competitive applications or dual-degree programs.
- MAT (Miller Analogies Test) is an alternative at some institutions.
Clinical Experience (Strongly Preferred or Required)
- Many programs, especially Nurse Practitioner or CRNA tracks, require 1–2 years of bedside nursing experience.
- Some may accept students without experience into generalist MSN or direct-entry programs.
Other Requirements
- Statement of Purpose (SOP)
- Letters of Recommendation
- Resume or Curriculum Vitae (CV)
Suggested Post: Masters in health administration in USA
Entrance Exams Required for Master’s in Nursing in the USA

When applying for a Masters in Nursing inUSA, entrance exam requirements depend on the type of program, school, and your academic background. While many programs have become test-optional in recent years, especially post-pandemic, some still require or recommend standardized tests.
1. GRE (Graduate Record Examination)
The GRE was once a standard requirement for many graduate programs in nursing, but over the past few years, most top MSN programs have waived it or made it optional.
When is GRE required?
- For dual-degree programs (e.g., MSN/MPH or MSN/MBA)
- At highly selective universities like Yale, Columbia, and Johns Hopkins (optional or recommended, not mandatory)
- If the applicant’s undergraduate GPA is low, the GRE can strengthen the application
GRE General Test Components:
- Verbal Reasoning (130–170)
- Quantitative Reasoning (130–170)
- Analytical Writing (0–6)
Tip:
Check each university’s program page. Many explicitly state: “GRE not required” or “GRE optional”.
2. NCLEX-RN (National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses)
The NCLEX-RN is not an entrance exam for MSN programs but plays a vital role in nursing licensure and career readiness.
When is NCLEX required?
- Before applying to an MSN program: If you’re pursuing a traditional MSN and already hold a BSN and RN license, you would have already passed the NCLEX.
- After graduation: If you’re enrolling in a Direct-Entry MSN (for non-nurses), you will typically take the NCLEX-RN during or after the program as part of your licensure process.
For International Students:
- If you plan to practice in the U.S. after earning your degree, passing the NCLEX-RN is mandatory for licensure in any U.S. state.
- You must have your foreign credentials evaluated (e.g., by CGFNS) before taking the NCLEX.
3. MAT (Miller Analogies Test)
The MAT is an alternative to the GRE and is accepted by a few nursing schools. However, it is less commonly used.
When is MAT required?
- Rarely required; only a handful of U.S. universities accept it in place of GRE
- It’s more common in MSN in Education or Leadership tracks
Suggested Post: Cost of MBBS in USA for Indian students
Top Universities for Masters in Nursing in USA
Choosing the right university is one of the most important decisions when pursuing a Master’s in Nursing (MSN) in the U.S. The country is home to several world-class nursing schools that offer cutting-edge education, diverse specialization options, clinical partnerships with top hospitals, and strong post-graduation employment rates.
Below is a list of top-ranked universities for nursing master’s programs, based on the latest data from U.S. News & World Report 2024, QS World Rankings, and program-level reputation.
| University Name | Specializations Offered | Avg. Tuition (Per Year) |
| Johns Hopkins University | NP, CNS, CNL, Education, Admin | $45,000–$52,000 |
| Duke University | FNP, Pediatric NP, AGNP, Health Leadership | $49,000–$53,000 |
| University of Pennsylvania | CRNA, Midwifery, NP, Education | $48,000–$54,000 |
| Emory University | Neonatal NP, FNP, Nurse Midwife | $45,000–$50,000 |
| University of Washington | NP, Public Health, Informatics | $35,000–$42,000 |
| Columbia University | FNP, Acute Care NP, Informatics | $50,000–$55,000 |
| University of Michigan–Ann Arbor | NP, CNS, Admin, Midwifery | $38,000–$45,000 |
| Yale University | Midwifery, PMHNP, Community Health | $48,000–$53,000 |
| Vanderbilt University | Dual NP Tracks, Nurse Informatics | $43,000–$47,000 |
| University of North Carolina–Chapel Hill | Pediatric NP, Geriatric NP, Leadership | $33,000–$40,000 |
Other Highly Respected Universities for MSN Programs
- Rush University (Chicago, IL): Strong in CRNA and NP programs
- Case Western Reserve University (Cleveland, OH): Known for clinical research and informatics
- Ohio State University: Offers affordable, high-ranking online MSN options
- University of California, San Francisco (UCSF): Excellent in midwifery, NP, and research tracks
- University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston: Popular among international students for its affordability
Clinical Partnerships and Practicum Sites
Top MSN programs in the U.S. often partner with:
- Johns Hopkins Hospital
- Mayo Clinic
- Massachusetts General Hospital
- NewYork-Presbyterian
- Cleveland Clinic
This gives students access to some of the best clinical training environments in the world.
Accreditation to Check Before Applying
Ensure the program is accredited by one of the following bodies:
- CCNE – Commission on Collegiate Nursing Education
- ACEN – Accreditation Commission for Education in Nursing
Accreditation is essential for licensure, financial aid, and employer recognition.
Suggested Post: MBBS in USA without NEET for Indian students
Program Duration and Structure of Masters in Nursing in USA
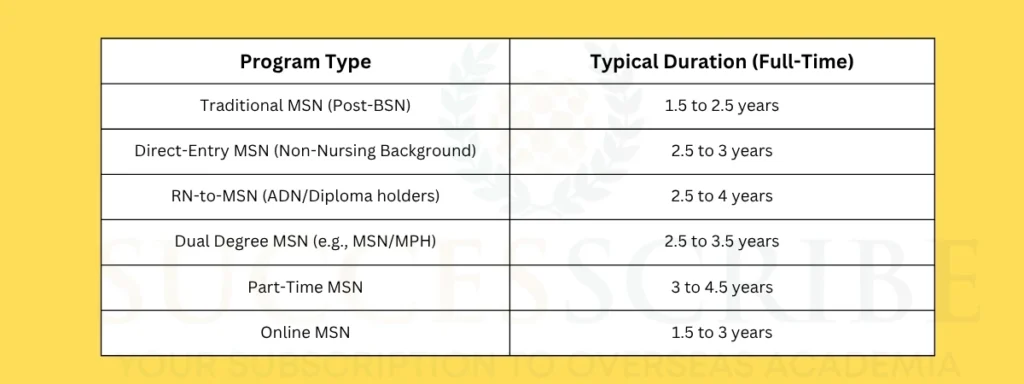
The duration and structure of a Master’s in Nursing (MSN) program in the United States vary depending on the type of program, entry point, and mode of delivery (full-time, part-time, or online). Understanding these variations is essential for planning your academic journey, clinical commitments, and career goals.
Duration of MSN Programs
| Program Type | Typical Duration (Full-Time) | Notes |
| Traditional MSN (Post-BSN) | 1.5 to 2.5 years | For RNs with BSN |
| Direct-Entry MSN (Non-Nursing Background) | 2.5 to 3 years | Includes pre-licensure phase |
| RN-to-MSN (ADN/Diploma holders) | 2.5 to 4 years | Varies by course load and bridge curriculum |
| Dual Degree MSN (e.g., MSN/MPH) | 2.5 to 3.5 years | Two degrees in one program |
| Part-Time MSN | 3 to 4.5 years | Designed for working nurses |
| Online MSN | 1.5 to 3 years | Clinical hours must be completed locally |
Accelerated Options: Some universities offer accelerated MSN programs for high-achieving students that compress coursework into as little as 12–16 months (e.g., Emory’s Accelerated MSN for those with a healthcare background).
General Curriculum Structure
MSN programs in the U.S. combine theoretical coursework, hands-on clinical training, and often a capstone project or thesis. Let’s break this down:
1. Didactic Coursework (Theory)
Core courses include:
- Advanced Pathophysiology
- Pharmacology for Advanced Nursing Practice
- Health Assessment
- Nursing Leadership & Policy
- Research Methods and Evidence-Based Practice
- Ethics in Advanced Nursing Practice
- Health Informatics
Specialization-specific courses vary, for example:
- FNP Track: Primary care, pediatric care, adult-gerontology
- Nurse Educator: Curriculum development, pedagogy
- PMHNP: Psychiatric assessment, therapy, psychopharmacology
2. Clinical Practice/Practicum
MSN programs typically require 500 to 800+ hours of supervised clinical practice depending on the specialization. These hours are completed in hospitals, clinics, community health centers, or other healthcare settings.
| Role | Clinical Hours Required |
| Nurse Practitioner (NP) | 500–750+ |
| Clinical Nurse Leader (CNL) | 400–500 |
| Nurse Educator | 200–300 |
| Nurse Midwife | 800–1000 |
Clinical placements are often arranged by the university but can also be coordinated by the student (especially in online programs).
Suggested Post: MD vs MBBS in USA for Indian students
Student Visa and Work Permits in the USA for Nursing Students
Once admitted into a Master’s in Nursing (MSN) program in the U.S., international students must secure the appropriate visa and understand the work opportunities available during and after their studies. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of the visa and work authorization process:
1. F-1 Student Visa – The Standard for International Students
The F-1 visa is the most common visa type for international students pursuing academic studies in the U.S., including MSN programs.
How to Get It:
- Receive Form I-20 from your U.S. university after acceptance.
- Pay SEVIS Fee (approx. $350).
- Schedule a visa appointment at the U.S. Embassy or Consulate.
- Attend the visa interview with all necessary documentation.
Required Documents for F-1 Visa:
- Valid passport
- Form I-20 (from the university)
- Admission letter
- Proof of financial support
- SEVIS fee payment receipt
- Academic transcripts and test scores
- Visa application (DS-160) confirmation page
2. Can Nursing Students Work While Studying in the U.S.?
Yes, but with restrictions:
On-Campus Jobs:
- Allowed up to 20 hours/week during academic sessions
- Up to 40 hours/week during breaks
Off-Campus Jobs:
You can’t work off-campus during the first academic year, but afterward, you may apply for:
- CPT (Curricular Practical Training)
- Work-integrated into your MSN curriculum
- Must be approved by the university
- Often used for internships or clinical placements
- OPT (Optional Practical Training)
- Temporary work authorization after graduation
- Can work for up to 12 months full-time
- If you’re in a STEM-designated program, you may be eligible for a 24-month OPT extension
Many MSN specializations that focus on Nursing Informatics or Healthcare IT are STEM-qualified, making OPT extension possible.
3. What Happens After Graduation? Work Permits and Licensure
To practice as a nurse in the U.S. after an MSN, you typically must:
Pass the NCLEX-RN (if not already licensed)
- Required for nursing licensure in all U.S. states
- Must apply through the State Board of Nursing
Get a Work Visa (H-1B or others)
- Many hospitals sponsor H-1B visas for qualified foreign-educated nurses
- H-1B cap-exempt organizations (like non-profit hospitals and universities) are more open to hiring international nurses
Suggested Post: Duolingo accepting universities in USA
Tuition Fees and Living Cost for Masters in Nursing in the USA
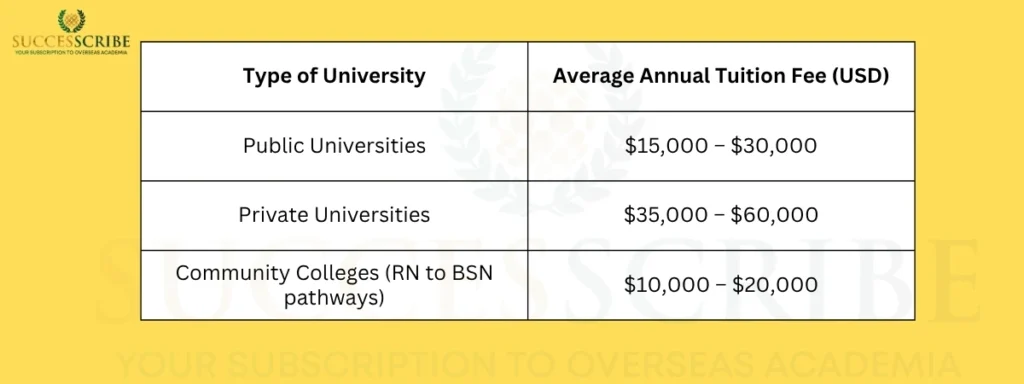
The tuition fee for Masters in Nursing in USA varies depending on the university, course structure, and whether it’s a public or private institution or Living costs largely depend on the location (urban cities like New York and LA are costlier than towns in the Midwest).
Tuition Fees
| Type of University | Average Annual Tuition Fee (USD) | Total for 2 Years (Approx.) |
| Public Universities | $15,000 – $30,000 | $30,000 – $60,000 |
| Private Universities | $35,000 – $60,000 | $70,000 – $120,000 |
| Community Colleges (RN to BSN pathways) | $10,000 – $20,000 | $20,000 – $40,000 |
Living Expenses
| Expense Category | Estimated Annual Cost (USD) |
| Housing (shared apartment) | $8,000 – $15,000 |
| Food and Groceries | $3,000 – $5,000 |
| Transportation | $600 – $1,200 |
| Health Insurance | $1,200 – $2,000 |
| Books and Supplies | $500 – $1,000 |
| Miscellaneous | $1,000 – $2,000 |
| Total (per year) | $14,000 – $26,000 |
Suggested Post: Dental hygienist course and universities in USA
Scholarships to Study Master’s in Nursing in the USA
International students often worry about the financial burden of studying in the USA. Fortunately, a wide variety of scholarships, grants, and financial aid options are available specifically for students pursuing a Master’s in Nursing. These scholarships are offered by universities, government programs, private foundations, and professional organizations.
- Fulbright Foreign Student Program
- AAUW International Fellowships (American Association of University Women)
- Nurse Corps Scholarship Program
- Sigma Theta Tau International Scholarships
- National Black Nurses Association (NBNA) Scholarships
- University-specific Scholarships (e.g., NYU, Johns Hopkins, Duke)
Scholarships for Indian Students
- Fulbright-Nehru Master’s Fellowships
- JN Tata Endowment for the Higher Education of Indians
- Inlaks Shivdasani Foundation Scholarships
- Narotam Sekhsaria Foundation Scholarship
- KC Mahindra Education Trust Scholarships
Suggested Post: Masters in biomedical engineering in USA
Career Prospects After Master’s in Nursing in the USA
Earning a Master’s in Nursing (MSN) in the USA opens doors to a wide range of high-paying, impactful, and leadership-oriented roles in healthcare. The U.S. healthcare system highly values advanced nursing professionals, and demand is growing rapidly due to aging populations, healthcare reforms, and provider shortages.
Top Career Roles and their Salaries After MSN in the USA
| Job Role | Average Salary (USD/year) |
| Nurse Practitioner (NP) | $110,000 – $140,000 |
| Clinical Nurse Specialist (CNS) | $90,000 – $120,000 |
| Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA) | $180,000 – $220,000 |
| Nurse Midwife | $100,000 – $120,000 |
| Nursing Administrator/Manager | $90,000 – $130,000 |
| Nursing Educator (University Level) | $75,000 – $100,000 |
| Public Health Nurse/Policy Advisor | $80,000 – $110,000 |
| Informatics Nurse Specialist | $90,000 – $125,000 |
Conclusion
Did you know that the United States is expected to need over 275,000 additional registered nurses by 2030? And that a nurse with a master’s degree in the U.S. can earn up to $135,000 per year depending on their specialization?
These numbers are not just statistics, they’re a call to action. A Masters in Nursing in USA is not just a degree; it’s a transformative journey that equips you with advanced clinical skills, leadership capabilities, and the power to directly influence the future of healthcare, locally and globally. If you’re ready to lead the future of healthcare, your journey starts here.
FAQs
What is the eligibility to pursue a Master’s in Nursing in the USA?
To be eligible, most universities require:
1. A Bachelor’s in Nursing (BSN) or equivalent
2. A valid Registered Nurse (RN) license
3. A minimum GPA of 3.0 on a 4.0 scale
4. English proficiency test scores (IELTS, TOEFL)
5. Letters of recommendation and a personal statement
Can I do a Master’s in Nursing in the USA without a BSN?
Yes, some universities offer entry-level MSN programs or direct-entry MSN programs for students with a non-nursing bachelor’s degree. However, you may need to complete prerequisite courses first.
Is the NCLEX-RN required for international students?
If you plan to work as a registered nurse in the U.S. after your MSN, yes, you’ll need to pass the NCLEX-RN exam and meet state licensure requirements.
Is the GRE required for MSN admissions in the USA?
In most cases, no. Many nursing schools have dropped the GRE requirement. However, a few top-tier programs may still ask for it, always check the latest admission criteria of your target schools.
Will my Indian RN license be valid in the USA for MSN?
No, but that’s okay. While your Indian RN license isn’t directly transferable, it helps demonstrate your clinical background. To practice as an RN in the U.S., you’ll need to pass the NCLEX-RN and meet the state-specific Board of Nursing requirements.
Related Post
Chemical engineering in USA
Cost of MBBS in USA for Indian students
Bachelor in Computer Science in USA
Engineering management courses in USA















