Community colleges in the United States play a vital role in making higher education accessible, affordable, and career-oriented. For decades, they have served as an entry point into the American education system for millions of students, including domestic learners, working professionals, and a growing number of international students. As of 2026, community colleges in USA continue to evolve by offering flexible learning pathways, strong industry alignment, and cost-effective education without compromising academic quality.
For Indian and international students who wish to study in the USA but are concerned about high tuition fees, competitive admissions, or long study durations, community colleges provide a practical and reliable alternative. These institutions focus on associate degrees, certificates, workforce training, and university transfer programs that open doors to both employment and further education.
Key Highlights: Community Colleges in USA
- What Are Community Colleges? (US Education System Explained)
- History and Growth of Community Colleges in the United States
- How Many Community Colleges Are There in the USA?
- Types of Programs Offered by Community Colleges
- Popular Courses at Community Colleges in the USA
- Top Community Colleges in USA for International Students
- Cost of Studying at Community Colleges in the USA
- Scholarships for Community Colleges in the USA
- Admission Requirements for Community Colleges in USA
- Community Colleges vs Universities in USA
- Transfer System: Community Colleges to Universities
- Career Opportunities After Community College
- Advantages of Studying at Community Colleges in the USA
- Limitations & Challenges at Community Colleges in USA
- Myths vs Facts About Community Colleges in the USA
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Want to Study in Europe?
Start your journey with Successcribe’s free expert guidance
Book a Free Session NowWhat Are Community Colleges? (US Education System Explained)

Community colleges are public, two-year higher education institutions primarily funded by state and local governments. They are designed to serve local communities while maintaining open or minimally selective admissions policies.
At their core, community colleges in USA are primarily public, two-year institutions of tertiary education. Historically, they were often referred to as “junior colleges,” a term now more commonly associated with private two-year schools. The primary credentials they offer are the Associate of Arts (AA) and Associate of Science (AS) degrees, which typically require two years of full-time study to complete. In addition to these degrees, they provide an extensive array of technical certificates, diplomas, and specialized vocational training programs.
This diverse range of offerings reflects their dual mission:
- Academic Transfer: Preparing students with the foundational coursework necessary to transfer seamlessly to a four-year university and complete a bachelor’s degree.
- Workforce Development: Equipping students with the practical, in-demand skills needed for immediate entry into the workforce.
For an international student, this dual mission provides a unique safety net: you can pursue a high-value transfer path while simultaneously gaining practical skills that may be valuable for OPT or your home country’s job market. To fully appreciate their current role, it is essential to understand their historical development.
History and Growth of Community Colleges in the United States
The concept of community colleges emerged in the early 20th century to expand access to higher education beyond elite universities. The first community college was established in 1901 in Illinois.
Major growth milestones include:
- 1940s – 1950s: Rapid expansion after World War II to support returning veterans
- 1960s – 1970s: Strong government investment to promote affordable education
- 2000s – present: Increased focus on workforce training, technology, and international students.
By 2026, community colleges have become central to the US education system, particularly in addressing skills gaps and promoting social mobility.
How Many Community Colleges Are There in the USA?
The scale and impact of community colleges are evident in their sheer numbers and the millions of students they serve. These institutions form a vast network that makes higher education accessible in nearly every region of the country.
There are over 1,000 community colleges in USA, with some sources citing a total of 1,166 institutions. While they remain a cornerstone of the U.S. education system, their enrollment has shifted in the last decade.
According to enrollment data cited by Wikipedia from the National Student Clearinghouse, community college enrollment has declined each year since its peak in 2010.
- In 2010, enrollment stood at 7,030,516 students.
- By 2020, that number had fallen to 4,824,204 students.
- This represents a total decline of over 2.2 million students over the decade.
Despite these recent trends, community colleges continue to educate a significant portion of the nation’s undergraduates and remain a critical component of the U.S. higher education landscape.
Suggested Post: Profile building bachelors in USA
Types of Programs Offered by Community Colleges
The modern “comprehensive community college” is designed to be a versatile educational hub, offering a wide array of programs that cater to diverse student goals. Whether a student seeks a direct path to a four-year university or immediate employment, there is a program designed to meet that need.
1. Associate Degrees
Associate degrees are the most popular qualification offered by community colleges.
Duration: 2 years
Types include:
- Associate of Arts (AA) – humanities, social sciences
- Associate of Science (AS) – STEM and technical fields
- Associate of Applied Science (AAS) – career-focused programs
2. Certificate Programs
Certificate programs are short-term, skill-based courses designed for quick employment.
Duration: 6 months to 1 year
Popular fields include IT support, healthcare assistance, business operations, and skilled trades.
3. Diploma & Vocational Courses
These programs focus on hands-on training and industry readiness.
Examples:
- Automotive technology
- Culinary arts
- Electrical and HVAC training
4. Workforce & Skill-Based Training
Community colleges work closely with industries to design customized training programs for:
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing
- Logistics
- Information technology
Duration of Community College Programs
| Program Type | Duration |
| Associate Degree | 2 years |
| Certificate | 6–12 months |
| Diploma/Vocational | 1–2 years |
Suggested Post: Bank for international students in USA
Popular Courses at Community Colleges in the USA
The popularity of specific programs at community colleges is often driven by regional economic demands, workforce needs, and established transfer pathways to four-year universities. International students will find a wide variety of robust programs across many fields of study. Note the strong emphasis on both STEM & Technology and Skilled Trades. This reflects the community college mission to fuel local economies, offering international students direct pathways into fields with high demand for practical training and potential OPT opportunities.
Based on current trends and program offerings, some of the most popular fields of study for the 2026 academic year include:
Business & Management
- Business Administration
- Management
- Marketing
- Accounting
Healthcare
- Nursing (Registered Nurse programs)
- Allied Healthcare (e.g., dental assistants, medical assistants)
- Radiation Therapy
- Biomedical Technology
STEM & Technology
- Engineering Technology
- Computer and Information Sciences
- Web Development
- Robotics and Laser Optics
- Geosciences
Liberal Arts & Social Sciences
- Liberal Arts (General Studies for transfer)
- Psychology
- Social Sciences
Skilled Trades
- Automobile Mechanics
- Electrician
- Paralegal Studies
Top Community Colleges in USA for International Students

While the concept of a “top” community college is subjective and depends heavily on a student’s individual goals, several institutions are consistently well-regarded and frequently mentioned as excellent choices for international students. These colleges are often recognized for their strong academic programs, robust student support services, and successful transfer records. The following table lists a selection of these notable colleges
| College Name | Location | Noted For (Based on Source Context) |
| Santa Monica College | Santa Monica, CA | A top-ranked college for transfers to the prestigious University of California (UC) system. |
| The City University of New York (CUNY System) | New York City, NY | A large, diverse system of community colleges located across the five boroughs of NYC. |
| Miami Dade College | Miami, FL | One of the largest and most innovative colleges in the U.S., located in a major multicultural city. |
| Diablo Valley College | Pleasant Hill, CA | Strong and well-established transfer pathways to the UC and California State University (CSU) systems. |
| Northern Virginia Community College | Annandale, VA | A large, multi-campus institution with diverse programs located near Washington, D.C. |
| Houston Community College | Houston, TX | Noted for its affordability and diverse program offerings in a major metropolitan area. |
| South Texas College | McAllen, TX | Known for its affordable tuition and strong programs in fields like Business Administration and Engineering. |
| Bergen Community College | Paramus, NJ | A comprehensive college with strong transfer options, located in close proximity to New York City. |
| Lane Community College | Eugene, OR | A well-regarded institution with diverse programs located in the Pacific Northwest. |
| Harper College | Palatine, IL | A comprehensive community college with strong workforce programs in the Chicago metropolitan area. |
Apply to Top European Universities
Make your application simple and stress-free with Successcribe
Get Expert Help NowCost of Studying at Community Colleges in the USA
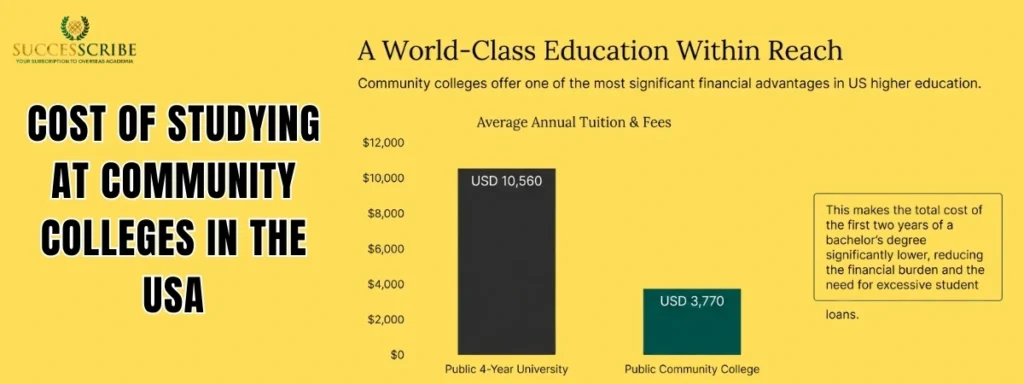
Affordability is one of the most compelling advantages of the community college pathway, especially for international students. The cost savings are substantial when compared to beginning studies at a traditional four-year university. This section provides a clear breakdown of the associated costs.
Tuition Fees at
Tuition at public community colleges is significantly lower than at public four-year universities. For the 2026 academic year:
| Average Tuition & Fees | Public Community College | Public Four-Year University (In-State, Annual) |
| Average Tuition & Fees | $4,050 | $10,560 |
| Average Total Cost of Attendance | $20,570 | $27,146 |
Suggested Post: Exams required to study in USA
Scholarships for Community Colleges in the USA
A common misconception is that financial aid and scholarships are scarce for community college students. In reality, numerous scholarship opportunities exist to make this already affordable option even more accessible. Many states and individual colleges have established programs to reduce or eliminate the cost of attendance for eligible students.
A significant development in recent years has been the rise of “College Promise” programs. These initiatives, which exist in dozens of states, offer tuition-free community college to qualified residents. Prominent examples include:
- The Tennessee Promise, a scholarship and mentoring program that covers tuition and fees not covered by other aid.
- The Oregon Promise, a state grant that helps cover most tuition costs at any Oregon community college for recent high school graduates.
- The California College Promise Grant, which waives enrollment fees for eligible California residents.
While many of these programs are targeted at state residents, they demonstrate the strong public support for making community college education affordable. International students should research scholarships offered directly by their prospective colleges, many of which have aid specifically for international applicants.
Admission Requirements for Community Colleges in USA
Community colleges in USA are widely known for their “open admissions” policy, which makes them highly accessible institutions. The goal is to provide an opportunity for higher education to anyone who can benefit from it. While this simplifies the process, international students must still meet a set of specific documentation and proficiency requirements to secure admission and obtain a student visa.
For US Students
For domestic students, the primary requirement for admission is typically a high school diploma or a General Educational Development (GED) certificate. Some colleges may also admit students who can demonstrate an “ability to benefit” from the instruction, even without a diploma.
For International Students
International applicants must provide a more extensive set of documents to verify their academic background, English proficiency, and financial standing. A typical application package includes:
- Completed Online Application Form
- Official High School Transcripts and Certificates (translated into English, if necessary)
- Proof of English Language Proficiency
- Standardized Test Scores (SAT/ACT), if required by the specific college or program
- Copy of a valid Passport
- Proof of Sufficient Funds (e.g., official bank statements) to cover educational and living expenses
- Health Insurance
- Statement of Purpose (SOP) or personal essay
- Letters of Recommendation (LOR), if required
English Language Requirements (IELTS, TOEFL, Duolingo)
Demonstrating English proficiency is a mandatory step for students from non-English speaking countries. Community colleges commonly accept scores from the following standardized tests:
| Test | Minimum Score |
| IELTS | 5.5 – 6.0 |
| TOEFL iBT | 61 – 70 |
| Duolingo | 85 – 95 |
Visa Requirements for Community College Students (F-1 Visa)
To study in the United States, all international students must obtain the proper visa.
- F-1 student visa
- I-20 from SEVP-approved college
- Proof of funds
- Academic intent
Community Colleges vs Universities in USA
Choosing between a community college and a four-year university is a significant decision. Each institution type plays a distinct role in the U.S. higher education system and offers a different student experience. The table below distills the key differences to help you determine which path best aligns with your academic goals, learning style, and financial circumstances.
| Feature | Community College | Four-Year University |
| Primary Degree | Associate Degree (2 years) | Bachelor’s Degree (4 years) |
| Admission Policy | Open admissions (typically requires HS diploma/GED) | Selective admissions (based on GPA, test scores, essays) |
| Average Annual Tuition | $4,050 | $10,560 (public, in-state) |
| Class Size | Generally smaller (e.g., 20-30 students) | Can be very large, especially introductory courses (300+) |
| Faculty Focus | Primarily teaching and student support | A mix of teaching and academic research |
| Student Body | Diverse in age (average 28) and background; many part-time | Primarily 18-22 year olds; more full-time students |
| Primary Mission | Workforce training, community education, and transfer pathway | Bachelor’s, graduate, and doctoral education; academic research |
Transfer System: Community Colleges to Universities
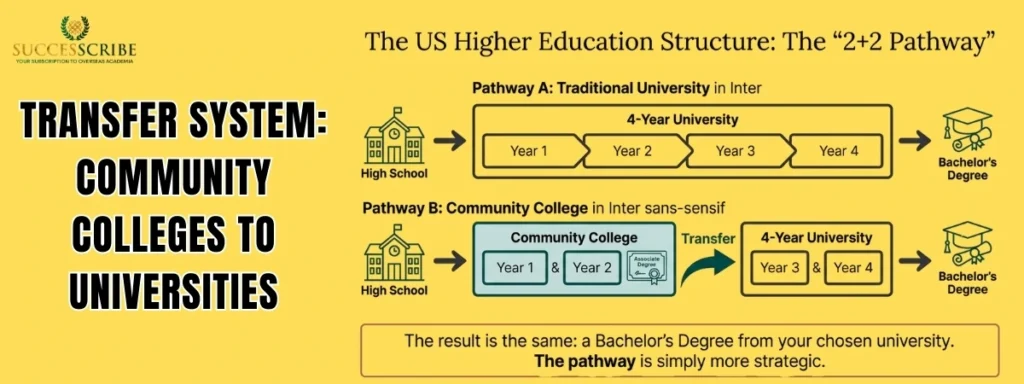
The structured transfer system within Community Colleges in USA enables students to complete the first half of their bachelor’s degree affordably before moving to a four-year university through established articulation agreements. This well-established pathway, often referred to as the “2+2 model,” makes a prestigious university degree more accessible and affordable. This section details how the transfer system works.
2+2 Pathway Explained
The “2+2 process” is a straightforward academic plan:
- A student enrolls at a community college and completes the first two years of their undergraduate coursework, earning an associate degree.
- The student then applies and transfers to a four-year university as a junior (third-year student).
- The student completes the final two years of coursework at the university, earning a bachelor’s degree.
This model allows students to save significantly on tuition for the first half of their degree while benefiting from smaller classes and a supportive learning environment.
Transfer Agreements
To ensure a smooth transition, many community colleges and universities establish formal partnerships known as Articulation Agreements. These agreements guarantee that the credits earned for specific courses at the community college will be accepted and applied toward a bachelor’s degree at the partner university.
Some states have created comprehensive, statewide transfer systems to simplify the process even further. Notable examples include:
- ASSIST (Articulation System Stimulating Interinstitutional Student Transfer) in California.
- The I-transfer program in Illinois.
- The Texas Common Course Numbering System (TCCN).
Career Opportunities After Community College
Graduates of Community Colleges in USA benefit from job-ready skills and strong employability, particularly in technical and healthcare roles aligned with local and national workforce needs.
Salary Data
While a bachelor’s degree generally leads to higher lifetime earnings, an associate degree provides a significant earnings boost over a high school diploma and can lead to a financially stable career. According to 2022 earnings data from the National Center for Education Statistics:
- The median annual earnings for full-time workers aged 25-34 with an associate degree were $49,500.
- This compares to $66,600 for those with a bachelor’s degree.
Crucially, graduates with technical associate degrees in high-demand fields can often earn salaries that exceed those of individuals with bachelor’s degrees in less specialized fields.
Employability Trends
Community college graduates are highly employable because their training is directly aligned with current job market needs. Some of the promising career prospects that an associate degree or certificate can lead to include:
- Radiation Therapist
- Engineering Technician
- Registered Nurse
- Web Developer
- Dental or Legal Assistant
- Automotive Mechanic
- Electrician
Advantages of Studying at Community Colleges in the USA
For an international student, choosing the community college pathway is a strategic decision with a compelling set of benefits. This route offers a smart, practical, and supportive entry into the American higher education system. The advantages are numerous and significant.
- Significant Cost Savings
- Accessible Admissions
- Smaller Class Sizes & Personalized Attention
- Flexible Scheduling
- A Proven Pathway to Top Universities
- Practical Skill Development
- Supportive Learning Environment
Limitations & Challenges at Community Colleges in the USA
While the community college pathway offers many clear advantages, it is important for prospective students to be aware of potential challenges to make a fully informed decision. Acknowledging these limitations allows for better planning and a higher likelihood of success.
- Transfer Credit Issues
- High Reliance on Part-Time Faculty
- Lower Completion Rates
- Social Stigma
Myths vs Facts About Community Colleges in the USA
As your advisor, it is my job to help you separate outdated myths from the modern reality. Many misconceptions can prevent students from making a smart strategic choice. Let’s debunk them with facts.
| Myth | Fact |
| “Community college is not ‘real’ college.” | Community college courses provide legitimate college-level credit. These credits are widely accepted for transfer to four-year universities, and faculty are required to hold advanced degrees (master’s or doctoral) in their field. |
| “You can’t get into a good university from a community college.” | Community colleges have formal transfer agreements with top state and private universities. Transfer students who have proven their academic abilities often have a strong admissions profile and high rates of success after transferring. |
| “The education quality is lower.” | Classes are smaller and taught by professors whose primary focus is teaching, not research. This often results in more personalized attention and dedicated instruction than students receive in large introductory courses at research universities. |
| “It’s only for vocational or trade jobs.” | Community colleges are comprehensive institutions. In addition to career and technical education, they offer robust transfer programs in liberal arts, social sciences, business, and STEM fields that form the foundation of a bachelor’s degree. |
Conclusion
Overall, Community Colleges in USA represent one of the most strategic and practical entry points into American higher education, particularly for international students seeking affordability, flexibility, and long-term academic growth. By providing accessible admissions, significant cost savings, and a proven transfer pathway to world-class universities, they represent one of the most strategic and intelligent choices a prospective student can make. We encourage you to use this guide as a foundational resource as you embark on your research and begin your application journey toward a successful future.
FAQs
What is an associate degree?
An associate degree is a two-year undergraduate degree (e.g., Associate of Arts or Associate of Science) that serves as the foundation for a bachelor’s degree or prepares students for direct entry into the workforce.
How much can I really save by starting at a community college?
The savings are substantial. Average annual tuition at a community college is around $4,050, compared to $10,560 at a public four-year university. Over two years, this can save you over $13,000 in tuition alone.
Do I need to take the SAT or ACT?
It depends on the college. Many community colleges have an open admissions policy and do not require the SAT or ACT, but some specific programs might. Always check the requirements for the institutions you are interested in.
Are the professors at community colleges qualified?
Absolutely. Community college professors are required to have advanced degrees, such as a master’s or a doctorate, in their field. Their primary focus is on teaching and student support.
Can I get a scholarship to attend a community college?
Yes. Many scholarships are available, including state-level “College Promise” programs that can make college tuition-free for eligible students, as well as institutional aid specifically for international students.
Related Post
Education loan for USA
Education system in USA
Data science courses and universities in USA
Commerce courses and colleges in USA














