The United States has consistently positioned itself as the global leader in undergraduate education, innovation, and research-driven learning. In 2026, this dominance is not accidental – it is the outcome of a deeply integrated ecosystem that connects universities, industries, startups, research labs, and global employers.
A Bachelors Degree in USA is globally perceived as a high-value academic and professional credential. Unlike many education systems that focus narrowly on theoretical learning, US undergraduate education emphasizes critical thinking, interdisciplinary exposure, real-world application, and long-term career readiness.
Key Highlights: Bachelors Degree in USA
- Understanding the US Bachelor’s Degree System
- Types of Bachelor’s Degrees in the USA
- Types of Institutions Offering Bachelor’s Degrees
- Popular Bachelor’s Courses in the USA
- Top Universities for Bachelors Degree in the USA
- Admission Requirement: Bachelors Degree in the USA
- Scholarships for Bachelor’s Degree in USA
- Actual Cost of Studying for a Bachelor’s Degree in USA
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Understanding the US Bachelor’s Degree System
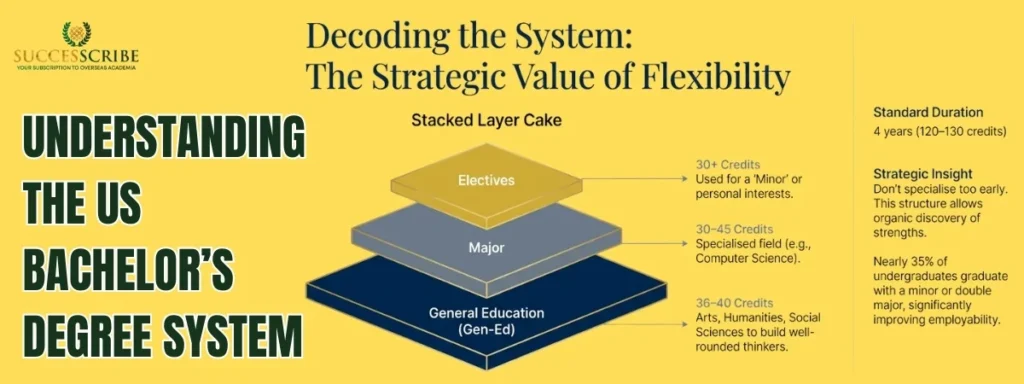
The US undergraduate education model is designed around academic flexibility and intellectual exploration, making it fundamentally different from rigid systems in many other countries.
Duration & Credit System
- Standard duration: 4 years
- Total credits required: 120 – 130 credits
- Each course usually carries 3 – 4 credits
- Students take general education + major + electives
The Credit Hour & GPA System
In 2026, the standard for a Bachelor’s degree remains 120 to 128 semester credits.
- Major Requirements: 30 – 45 credits in your specialized field.
- General Education (Gen-Ed): 36 – 40 credits in diverse subjects (Arts, Humanities, Social Sciences, Natural Sciences).
- Electives: 30+ credits to spend on a “Minor” or personal interests.
This structure ensures students do not specialize too early, allowing them to discover interests and strengths organically.
Major, Minor & Double Major System
- Major: Primary field of study (e.g., Computer Science)
- Minor: Secondary specialization (e.g., Economics)
- Double Major: Two full majors (e.g., CS + Mathematics)
Nearly 35% of US undergraduates graduate with a minor or double major, significantly improving employability.
Liberal Arts Philosophy
US universities strongly believe that great professionals are also well-rounded thinkers. Therefore, even engineering or business students study:
- Writing & communication
- Ethics
- Social sciences
- Humanities
- Quantitative reasoning
This is one reason US graduates are highly valued in leadership and management roles worldwide.
Want to Study in Europe?
Start your journey with Successcribe’s free expert guidance
Book a Free Session NowTypes of Bachelor’s Degrees in the USA
US universities offer degree titles aligned with industry outcomes, not just academic tradition. When pursuing a Bachelors Degree in USA, students can choose between academic tracks like the BA and BS or professional tracks like the BBA and BEng, with many opting for STEM-designated programs to maximize post-graduation work benefits.
Academic vs Professional Degrees
- Academic Degrees (BA, BS) – Research, academia, corporate roles
- Professional Degrees (BBA, BSN, BEng) – Direct industry application
STEM vs Non-STEM Impact
STEM classification has major immigration and career implications.
| Degree Type | STEM Status | OPT Duration | Career Advantage |
| Computer Science | STEM | 36 months | Very High |
| Engineering | STEM | 36 months | Very High |
| Data Science | STEM | 36 months | Extremely High |
| Business Analytics | STEM | 36 months | High |
| Economics | Often STEM | 36 months | High |
| Psychology | Non-STEM | 12 months | Moderate |
Over 55 – 60% of international bachelor’s students now choose STEM degrees primarily due to extended OPT benefits.
Types of Institutions Offering Bachelor’s Degrees
The United States hosts over 4,300 degree-granting institutions, each offering unique advantages. Public universities, funded by state governments, typically offer lower tuition rates for in-state students but charge higher fees for out-of-state and international students. Private universities operate independently and charge the same tuition regardless of residency status. Liberal arts colleges focus on undergraduate education with smaller class sizes and emphasize critical thinking and broad-based learning. Community colleges offer two-year associate degrees that can transfer to four-year institutions, providing a cost-effective pathway to a bachelor’s degree.

Institution Types Comparison
From large public research universities to intimate liberal arts colleges, the variety of institutions offering a Bachelors Degree in USA ensures that every student can find a campus culture and tuition structure that fits their needs.
| Institution Type | Average Annual Tuition | Typical Class Size | Key Advantages |
| Public University (In-State) | $11,260 | 50-200 students | Affordable, diverse programs, research opportunities |
| Public University (Out-of-State) | $29,150 | 50-200 students | Wide program variety, strong athletics, large alumni networks |
| Private University | $42,162 | 20-50 students | Smaller classes, generous financial aid, prestige |
| Liberal Arts College | $38,500 | 15-25 students | Personal attention, undergraduate focus, critical thinking emphasis |
| Community College | $3,990 | 25-35 students | Lowest cost, transfer pathways, flexible scheduling |
Popular Bachelor’s Courses in the USA
The USA offers one of the widest ranges of bachelor’s programs globally, designed to align closely with future job markets, industry needs, and global career pathways. In 2026, international students are increasingly choosing courses that provide strong employability, STEM advantages, and long-term return on investment (ROI).
Most In-Demand Bachelor’s Courses
| Course / Major | Degree Type | STEM Status | Career Demand | Avg Starting Salary |
| Computer Science | BS | STEM | Very High | $80,000 – $95,000 |
| Engineering (All Branches) | BEng / BS | STEM | High | $70,000 – $85,000 |
| Data Science & AI | BS | STEM | Extremely High | $85,000 – $100,000 |
| Business Administration | BBA / BS | Non-STEM | High | $60,000 – $70,000 |
| Business Analytics | BS | STEM | Very High | $70,000 – $85,000 |
| Economics | BA / BS | Often STEM | High | $65,000 – $75,000 |
| Psychology | BA / BS | Non-STEM | Moderate | $50,000 – $60,000 |
| Life Sciences / Biology | BS | STEM | High | $55,000 – $65,000 |
| Nursing (BSN) | BSN | STEM | Very High | $70,000 – $85,000 |
| Liberal Arts | BA | Non-STEM | Moderate | $45,000 – $55,000 |
Course Popularity by Student Preference
| Category | Why Students Choose It |
| STEM Courses | 36-month OPT, high-paying jobs |
| Business & Economics | Leadership & management careers |
| Healthcare | Job security & demand |
| Liberal Arts | Flexibility & interdisciplinary learning |
Top Universities for Bachelors Degree in USA
Selecting the “best” university is a deeply personal decision that depends on academic fit, career goals, campus culture, and financial reality. The U.S. higher education landscape in 2026 is characterized by both enduring excellence at established institutions and the rapid rise of universities making significant investments in student outcomes and research.
| Rank | University | Location | Key Strength / “Flagship” Major | Est. Tuition (International) |
| 1 | Princeton University | Princeton, NJ | Public Policy, Economics, CS | $65,210 |
| 2 | MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) | Cambridge, MA | AI, Robotics, Engineering | $62,500 |
| 3 | Harvard University | Cambridge, MA | Law, Medicine, Humanities | $61,000 |
| 4 (tie) | Stanford University | Stanford, CA | Entrepreneurship, Tech, Bio-Sci | $67,730 |
| 4 (tie) | Yale University | New Haven, CT | History, Arts, Political Science | $66,500 |
| 6 | University of Chicago | Chicago, IL | Economics, Sociology, Math | $68,100 |
| 7 | Johns Hopkins University | Baltimore, MD | Biomedical Engineering, Nursing | $64,200 |
| 8 | University of Pennsylvania (UPenn) | Philadelphia, PA | Business (Wharton), Fintech | $66,800 |
| 9 | California Institute of Tech (Caltech) | Pasadena, CA | Physics, Aerospace Engineering | $63,000 |
| 10 | Duke University | Durham, NC | Biology, Public Policy, Finance | $65,800 |
Elite institutions like Princeton, MIT, and Harvard lead the rankings for a Bachelors Degree in USA, though public powerhouses like UC Berkeley and UCLA have become equally competitive for engineering and social mobility.
Why These Schools Lead
- The “AI-Ready” Curriculum: In 2026, MIT and Stanford have reclaimed the top spots because they have fully integrated AI literacy into every major. An English major at Stanford now learns natural language processing, while a Finance major at MIT uses predictive AI models.
- Public vs. Private Excellence: While the table above focuses on private “Ivies,” the 2026 rankings show a massive surge for Public Universities.
- UC Berkeley (#15) and UCLA (#17) are now ranked higher than many traditional Ivy League schools for Engineering and Social Mobility.
- University of Michigan (#20) remains the “Gold Standard” for a large-scale, research-intensive public education.
- The “Social Mobility” Factor: Ranking agencies in 2026 (like Forbes and U.S. News) have increased the weight of “Student Debt to Salary” ratios. Universities like Rice (#17) and University of Florida (#30) are climbing because they offer lower tuition with high starting salaries for graduates.
Apply to Top European Universities
Make your application simple and stress-free with Successcribe
Get Expert Help NowAdmission Requirement: Bachelors Degree in USA

US universities employ holistic admissions processes, a comprehensive evaluation system that considers multiple dimensions of applicants rather than relying solely on academic metrics. This approach, practiced by over 92% of four-year institutions, assesses academic achievement, personal qualities, extracurricular involvement, and potential contributions to campus community. Admissions committees review applications through multiple rounds, with each application receiving 8-12 minutes of initial review and competitive applications undergoing committee discussion lasting 15-25 minutes.
The holistic process aims to build diverse, talented classes bringing varied perspectives and experiences. Understanding how admissions officers evaluate applications helps students present themselves authentically and strategically.
High School Curriculum Requirements
US universities expect students to complete rigorous secondary education with specific course distributions:
| Subject Area | Required Years | Recommended for Competitive Schools | Preferred Course Level |
| English/Language Arts | 4 years | 4 years | Honors/AP Literature, Composition |
| Mathematics | 3-4 years | 4 years through Calculus | AP Calculus AB/BC, IB Math HL |
| Laboratory Science | 2-3 years | 3-4 years | AP Biology, Chemistry, Physics |
| Social Studies/History | 2-3 years | 3-4 years | AP US History, World History |
| Foreign Language | 2-3 years | 4 years same language | AP/IB Language courses |
| Electives | 1-2 years | 2-3 years | Arts, Computer Science, Additional Sciences |
Competitive universities specifically seek students who challenge themselves with the most rigorous curriculum available at their schools. Taking 6-12 Advanced Placement (AP), International Baccalaureate (IB), or A-Level courses signals academic readiness. However, admissions officers evaluate rigor within the context of what courses your school offers – you won’t be penalized if your school provides limited advanced options.
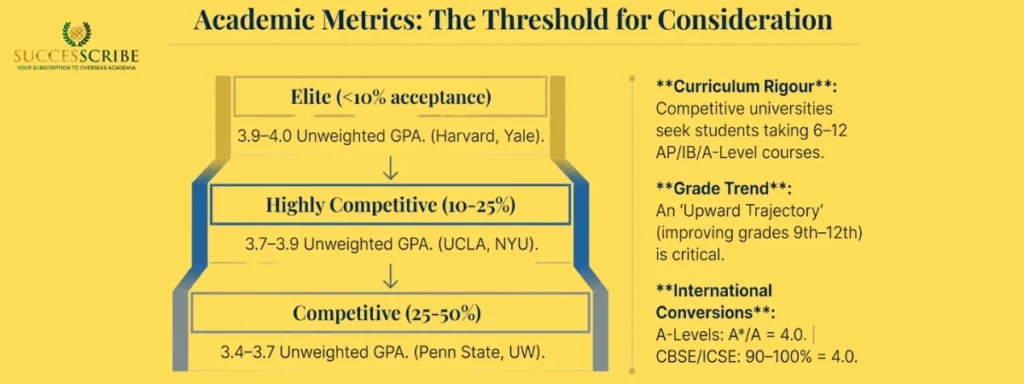
Grade Point Average (GPA) Expectations
GPA remains the single most important admission factor, with 89% of admissions officers rating it as considerably or moderately important. Here’s what different tiers of universities typically expect:
- Elite Universities (Acceptance Rate <10%): Unweighted GPA of 3.9 – 4.0, weighted GPA of 4.3 – 4.7. Examples include Harvard, Stanford, MIT, Princeton, Yale, Columbia. These institutions receive applications from students who could academically succeed anywhere, so GPA alone doesn’t guarantee admission.
- Highly Competitive Universities (Acceptance Rate 10-25%): Unweighted GPA of 3.7-3.9, weighted GPA of 4.0 – 4.3. Schools like University of California Berkeley, UCLA, University of Michigan, NYU, Boston University fall in this category.
- Competitive Universities (Acceptance Rate 25-50%): Unweighted GPA of 3.4-3.7, weighted GPA of 3.7 – 4.0. Examples include University of Washington, Penn State, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Texas A&M.
- Selective Universities (Acceptance Rate 50-70%): Unweighted GPA of 3.0-3.4. These include many excellent regional public universities and private colleges offering quality education.
- Academic Progression Matters: Admissions committees examine grade trends throughout high school. An upward trajectory (improving grades from 9th to 12th grade) demonstrates maturity and academic growth. Conversely, declining grades raise concerns about motivation and college readiness. Strong performance in 11th grade carries particular weight as it represents the most recent complete academic year before application.
International Credential Evaluation
International students must have their academic credentials evaluated to determine US equivalency. This process involves:
- Credential Evaluation Services: Organizations like World Education Services (WES), Educational Credential Evaluators (ECE), International Education Research Foundation (IERF), and SpanTran evaluate foreign transcripts. The evaluation costs $100-$250 and takes 2-4 weeks for standard processing, 1 week for rush service.
- Required Documents: Original or certified copies of mark sheets, diplomas, certificates, and grading scales from your institution. Documents not in English require certified translations by professional translation services, costing approximately $25-50 per page.
- Grading System Conversion: Evaluators convert your grades to the US 4.0 scale. Different countries use varying systems:
- UK A-Levels: A = 4.0, A = 4.0, B = 3.0, C = 2.0
- Indian CBSE/ICSE: 90-100% = 4.0, 80-89% = 3.7, 70-79% = 3.3
- Chinese 100-point scale: 90-100 = 4.0, 85-89 = 3.7, 80-84 = 3.3
- German Abitur: 1.0-1.5 = 4.0, 1.6-2.5 = 3.5, 2.6-3.5 = 3.0
SAT and ACT: College Readiness Tests
As of 2026, approximately 65% of four-year universities require standardized test scores for admission, with many institutions that went test-optional during 2020-2024 reinstating requirements. However, over 1,800 schools maintain test-optional or test-flexible policies, allowing students to decide whether to submit scores.
SAT Structure and Scoring
- Reading and Writing Section: 54 questions, 64 minutes, scored 200-800
- Math Section: 44 questions, 70 minutes, scored 200-800
- Total Score: 400-1600 (sum of two sections)
- Test Duration: 2 hours 14 minutes (versus 3 hours for paper SAT)
- Cost: $60 domestic, $68 international (without essay)
- Score Choice: Students can select which test dates to send to colleges
The digital SAT adapts difficulty based on performance, with each section containing two modules. Performance on the first module determines second module difficulty.
ACT Structure and Scoring:
- English: 75 questions, 45 minutes, scored 1-36
- Math: 60 questions, 60 minutes, scored 1-36
- Reading: 40 questions, 35 minutes, scored 1-36
- Science: 40 questions, 35 minutes, scored 1-36
- Optional Writing: 1 essay, 40 minutes, scored 2-12
- Composite Score: 1-36 (average of four sections)
- Cost: $68 without writing, $93 with writing (international fees higher)
Competitive Score Benchmarks by University Tier:
| University Category | SAT Score Range | ACT Score Range | Percentile |
| Elite (Top 20) | 1480-1580 | 33-35 | 99th percentile |
| Highly Competitive | 1380-1480 | 31-33 | 93-99th percentile |
| Competitive | 1200-1380 | 26-30 | 75-93rd percentile |
| Selective | 1060-1200 | 21-25 | 50-75th percentile |
| Less Selective | 900-1060 | 17-20 | 25-50th percentile |
English Language Proficiency Tests
International students from countries where English is not the primary language must demonstrate English proficiency. Some universities waive this requirement if students completed secondary education at English-medium institutions or scored above certain thresholds on SAT Reading/Writing (typically 650+)
| Test | 2026 Typical Competitive Score | Notes |
| IELTS Academic | 7.0+ (with 6.5+ in each band) | Preferred in Commonwealth countries. |
| TOEFL iBT | 100+ (with 22+ in each section) | Still the most widely accepted. Some top schools require 105+. |
| Exemptions | Usually granted for: 4+ years in an English-medium school; IB Diploma holders with high English A scores; citizens of Anglophone countries. | Always check the university’s specific waiver policy. |
Subject-Specific Tests: SAT Subject Tests and AP Exams
- SAT Subject Tests
College Board discontinued SAT Subject Tests in January 2021. However, some competitive programs (particularly in engineering and sciences) may still recommend subject proficiency demonstration through AP exams or IB Higher Level courses.
- AP Exams (Advanced Placement):
While primarily used for college credit, AP exam scores can strengthen applications, especially for international students lacking SAT/ACT scores. Over 60 AP exams span subjects from sciences to arts.
Scoring: 1-5 scale, with 3 considered “qualified,” 4 “well qualified,” and 5 “extremely well qualified”
Strategic AP Selection for Admissions:
- Take AP exams in subjects related to intended major
- Scores of 4-5 demonstrate mastery and college readiness
- Most competitive applicants submit 6-12 AP scores
- Self-studying for AP exams shows intellectual curiosity
College Credit: Many universities award credit for scores of 4-5, allowing students to skip introductory courses, save tuition costs, and graduate early or pursue double majors. Elite universities increasingly restrict AP credit to placement rather than course credit.
The Application Essays: Your Voice, Your Narrative
This is where you become more than a collection of data. The essays are the heart of the holistic review.
- The Personal Statement (Common App/Coalition App):
- Reflect on a background, identity, interest, or talent that is so meaningful you believe your application would be incomplete without it.
- Strategy (2026): Move beyond the “generic success story.” The most compelling essays show vulnerability, introspection, and growth. They answer “How do you think?” and “How do you learn from failure?” Topics centered on caregiving, community building, ethical dilemmas, or intellectual curiosity sparked by a simple event often resonate more than winning a competition.
- Supplemental Essays & “Why Us?” Essays:
- “Why Us?”: This is a research-intensive essay. It must move beyond rankings and campus beauty. Mention specific professors and their research (tie it to your interests), unique interdisciplinary majors or programs (e.g., “I want to combine my CS interest with ethics through your Technology & Society minor”), specific clubs, initiatives, or campus traditions. Demonstrate a fit that is both academic and cultural.
- Short-Answer Questions: Be concise, vivid, and authentic. For “Intellectual Interest” prompts, focus on the “why” behind your chosen major.
Letters of Recommendation (LORs): The External Validation
LORs provide a third-party, professional perspective on your character and potential.
Who to Ask: 1 Counselor Recommendation + 2 Teacher Recommendations (in core academic subjects from 11th or 12th grade). The ideal teacher is one in whose class you struggled initially and then improved significantly, or one where you contributed uniquely to classroom dialogue.
The 2026 Protocol: Provide your recommenders with a comprehensive “brag sheet” at least one month in advance. This should include:
- Your resume/CV.
- The specific programs/universities you’re applying to and deadlines.
- Key points you hope they might mention (e.g., “that time I led the group project after our teammate dropped out,” or “my improvement from a B to an A+ through office hours”).
- A copy of your personal statement.
Waiving Your Rights: Always waive your right to view the recommendations. This signals trust and ensures the letter is considered fully confidential and thus more credible.
Extracurricular Activities & Résumé: The “Doing” Complement to “Thinking”
The Common App allows listing 10 activities. Quality, depth, and impact trump a long list of superficial memberships.
The “Tier” System Admissions Officers Use (Unofficially):
- Tier 1: Rare, nation-level or international achievements. (Olympiad medals, nationally recognized artistic talent, founder of a impactful NPO).
- Tier 2: Demonstrated leadership and deep commitment. (Eagle Scout, Student Body President, Varsity Team Captain, Editor-in-Chief of school paper, research published in a legitimate journal).
- Tier 3: Meaningful involvement showing passion. (Section leader in orchestra, dedicated community service club member, math tutor).
- Tier 4: General membership/participation. (Member of 5 clubs with no leadership role).
2026 Focus: Initiative and “Spike.” Universities seek a “pointy” class composed of specialists. A student with a deep “spike” in computer science who has built apps for local businesses, contributed to open-source projects, and mentored younger coders is more compelling than a student with shallow involvement in eight unrelated areas.
Portfolios, Auditions, and Supplementary Materials
- Required for: Applicants to programs in Art, Architecture, Music, Theater, Film, and sometimes Creative Writing.
- Platform: Typically submitted via platforms like SlideRoom.
- Key Tip: Follow instructions meticulously for format, number of pieces, and descriptions. A portfolio should show technical skill, creativity, and conceptual thinking. Include process work.
The 2026 “Digital Footprint” Check
A new trend for 2026 admissions is the occasional review of an applicant’s professional digital presence.
- LinkedIn/Portfolio: For STEM and Business students, a link to a GitHub repository or a professional portfolio is now a common “optional” requirement.
- Social Media Audit: Ensure your public profiles reflect the values of the institution; many schools use automated sentiment analysis for “Red Flag” behavior.
Interviews: The Human Touch
- Alumni Interviews: Offered by many selective schools. These are evaluative but also informational. They rarely make or break an application but can confirm or raise doubts about fit.
- Preparation: Research the university deeply. Prepare thoughtful questions about the student experience, not easily found on the website. Practice talking about your interests with genuine enthusiasm. Be ready to discuss your essays.
Financial Documentation (F-1 Visa Requirements)
Before a university issues your I-20 (Certificate of Eligibility), you must prove you can afford the first year of study.
- Proof of Funds: Bank statements showing liquid cash (Savings, FDs) covering tuition + living expenses.
- Affidavit of Support: A signed legal document from your sponsor (parents/relatives) confirming they will fund your education.
- Scholarship Award Letter: If the university has granted you aid, this counts toward your proof of funds.
Scholarships for Bachelors Degree in USA
Pursuing a Bachelor’s degree in the USA can be a significant financial investment, but scholarships make US education more affordable and accessible for international students. As of 2026, US universities collectively distribute billions of dollars in undergraduate financial aid, and a large portion of this funding is available to international bachelor’s students, including students from India.
Unlike many countries, scholarships in the USA are mostly offered directly by universities, and students are automatically considered at the time of admission in most cases.
Types of Scholarships Available
- Merit-Based Scholarships
Awarded to students with strong academic performance, leadership qualities, or exceptional achievements.
- Based on grades, SAT/ACT scores (if submitted), and overall profile
- No separate application required at many universities
- Can range from USD 5,000 to full tuition per year
- Need-Based Financial Aid
Provided to students who demonstrate financial need.
- Assessed using family income and financial documents
- Available at select private universities
- Can significantly reduce total study cost
- Athletic Scholarships
For students with national or international-level sports achievements.
- Offered in sports such as football, basketball, tennis, swimming, and athletics
- May cover tuition, housing, meals, and training expenses
- Talent & Program-Specific Scholarships
Offered to students with excellence in:
- Music, arts, design, theatre
- STEM innovation or research
- Community service and leadership
Related Post: Fulbright scholarship in USA
Actual Cost of Studying for a Bachelor’s Degree in USA
The true cost of studying for a Bachelors degree in USA goes beyond tuition fees. Many students underestimate expenses like housing, health insurance, books, and daily living costs. In reality, the total annual cost depends on university type, location, lifestyle, and scholarships received.
On average, an international student should realistically budget between USD 45,000 and USD 80,000 per year before scholarships.
1. Tuition Fees (Biggest Expense)
Tuition varies widely based on whether the university is public or private.
| University Type | Annual Tuition (USD) |
| Public University (Out-of-State) | $25,000 – $45,000 |
| Private University | $40,000 – $65,000 |
| Community College | $8,000 – $15,000 |
Public universities are more affordable, while private universities often offer higher scholarships.
2. Living Expenses (Location Matters Most)
Living costs differ significantly by city and state.
| Expense | Annual Cost (USD) |
| Housing & Utilities | $8,000 – $14,000 |
| Food & Groceries | $3,000 – $5,000 |
| Transportation | $1,000 – $2,000 |
| Personal Expenses | $1,500 – $2,500 |
| Health Insurance (Mandatory) | $1,500 – $3,000 |
Cities like New York, San Francisco, Boston are expensive, while Texas, Arizona, Ohio are more budget-friendly.
Conclusion
A Bachelor’s Degree in the USA in 2026 offers unmatched academic flexibility, global recognition, industry exposure, and long-term career growth. While the investment is significant, the returns – in skills, salary, and global opportunities – are among the highest in the world. For students aiming to build global careers, innovate, or pursue advanced education, the USA remains the gold standard. Ultimately, obtaining a Bachelors Degree in USA remains the global gold standard for students seeking an interdisciplinary education that fosters innovation and prepares them for the leadership roles of the future.
FAQs
Is the SAT/ACT really mandatory again in 2026?
Yes, for most “Top 50” institutions. While the “Test-Optional” era hasn’t fully ended, elite schools like Harvard, Yale, and MIT have reinstated requirements to better assess academic rigor in the age of inflated high school grades.
What is the “Digital Footprint” check in admissions?
Some admissions officers now review public professional profiles (LinkedIn/GitHub) to see if your extracurricular claims match your online presence. It is highly recommended to have a clean, professional digital profile.
How much bank balance do I need for the F-1 Visa?
You must show liquid funds (cash in bank/fixed deposits) that cover at least the first 12 months of your total Cost of Attendance (Tuition + Living). For 2026, this typically ranges from $45,000 to $90,000 depending on the school.
How long is a Bachelor’s degree in the USA?
A Bachelor’s degree in the USA typically takes 4 years to complete. However, with Advanced Placement (AP), IB credits, or credit transfers, students may finish in 3–3.5 years depending on the university and course load.
Are scholarships available for Bachelor’s students in the USA?
Yes. International students can access:
1. Merit-based scholarships
2. University-specific awards
3. Need-based aid (limited)
4. Athletic and talent-based scholarships
Scholarship values typically range from USD 5,000 to full tuition coverage, depending on academic profile and university.
Related Post
Bachelor of Science in USA
Profile building bachelors in USA
Data science courses in USA
Duolingo accepting universities in USA













