Higher education institutions have been pillars of human civilization for over a millennium, shaping societies, advancing knowledge, and producing generations of scholars, leaders, and innovators. The oldest universities in the world represent not just ancient buildings and traditions, but living testaments to humanity’s enduring quest for knowledge and understanding. What makes these institutions remarkable is their resilience. Founded amid the Islamic Golden Age, the European Renaissance, and colonial expansions, they have evolved from modest madrasas and studium generale to sprawling campuses with satellite facilities across continents.
Key Highlights – Oldest Universities in the World
- Legacy of Learning: The world’s oldest universities—some over 1,000 years old – stand as symbols of humanity’s pursuit of knowledge and cultural exchange.
- Earliest Institutions: Al-Qarawiyyin (859, Morocco) and Al-Azhar (970, Egypt) are recognized by UNESCO as the oldest existing centers of higher learning.
- Europe’s First Universities: Bologna (1088), Oxford (1096), Paris (1150), Salamanca (1218), and Padua (1222) pioneered the modern university model.
- Oldest Medical Schools: From Salerno’s Schola Medica (9th–10th c.) to Montpellier (12th c.), these laid the foundation for modern medicine.
- Oldest Technical Universities: ČVUT (1707, Prague), École des Ponts (1747, France), and IIT Roorkee (1847, India) shaped early engineering education.
- Global Timeline: From Taxila and Nalanda to Oxford and MIT, the evolution of higher education spans Asia, Africa, and Europe.
- Modern Impact: These ancient institutions continue to thrive—driving innovation, sustainability, and global research collaborations.
What counts as a “university”? Definitions and criteria
Before listing institutions, we must agree a definition. Historians generally use two overlapping but distinct criteria:
- Medieval / European definition (universitas) – a corporate body of teachers and/or students with legal privileges and degree-granting powers (the classic medieval model). Universities in this set include Bologna, Paris (Sorbonne), Oxford, and Salamanca. This definition emphasizes legal form and continuous corporate identity.
- Broader “center of higher learning” definition – long-running institutions or traditions of advanced teaching (e.g., Nalanda, Taxila, the Islamic madrasas associated with Al-Qarawiyyin and Al-Azhar). These may not have used the Latin universitas model but were centers where advanced study and teaching of multiple disciplines occurred for centuries. UNESCO and Encyclopædia Britannica accept al-Qarawiyyin and Al-Azhar as the oldest surviving institutions of higher learning in their respective senses.
- Continuity – a crucial factor. Some ancient schools existed but were destroyed and later reconstituted under different legal forms; others claim ancient origins but gained “university” status only in the modern era (e.g., al-Qarawiyyin formally became a modern university in 1965 while tracing earlier roots to 859). That difference matters for how we rank “oldest university” vs. “oldest educational institution.”
List of Top Oldest Universities in the World

Below is a high-level overview of some of the most commonly mentioned institutions in discussions of the Oldest Universities in the World.
| Institution | Date of earliest foundation/teaching | Location | Key notes on continuity & status |
| University of al-Qarawiyyin | 859 CE | Fez, Morocco | Founded as a madrasa by Fatima al-Fihri; cited by UNESCO as oldest existing educational institution; became a modern university in 1965. |
| Al-Azhar University | c. 970–972 CE | Cairo, Egypt | Evolved from the al-Azhar mosque school; major center for Sunni Islamic learning; still active as a university. |
| University of Bologna | c. 1088 (teaching) | Bologna, Italy | Often cited as oldest European university in continuous operation; developed the medieval universitas model. |
| University of Oxford | c. 1096+ (teaching) | Oxford, United Kingdom | Teaching activity documented since late 11th–12th centuries; institutional continuity through modern era. |
| University of Paris (Sorbonne) | c. 1150 (school) / charter 1215 | Paris, France | One of the most important medieval universities; reorganized in modern era (1968 split). |
| University of Salamanca | 1218 (royal charter) | Salamanca, Spain | Oldest university in Spain; earlier roots pre-charter. |
| University of Padua | 1222 | Padua, Italy | Long continuous operation; early centre of medicine and science. |
Apply to Top German Universities
Make your application simple and stress-free with Successcribe
Get Expert Help NowDetailed List of Early Institutions
Here is a broader list of historic institutions that are often referenced among the Oldest Universities in the World. Because of variations in continuity and definitions, we indicate key caveats.
| Institution | Earliest date (foundation or documented teaching) | Region | Continuity / Comments |
| University of al-Qarawiyyin | 859 CE | Morocco (North Africa) | Founded as madrasa; recognized by UNESCO and Guinness as oldest existing degree-granting institution; modern university status from 1965. |
| Al-Azhar University | c. 970–972 CE | Egypt | Began as Islamic mosque school; evolved into modern university; long tradition of scholarship. |
| Nalanda Mahāvihāra | c. 5th century CE (approx. 427) | Bihar, India | Ancient Buddhist monastic university; destroyed in the 12th century; no continuous modern institution. |
| Taxila (Takṣaśilā) | circa 6th-5th century BCE (site of higher education) | Pakistan (ancient Gandhara) | Pre-university centre of learning; not a medieval university, and lacks continuous institutional identity. |
| University of Bologna | c. 1088 (teaching) | Italy | Widely regarded as oldest European university; continuous existence as a degree-granting university. |
| University of Oxford | c. 1096–1100s | UK | Teaching by 11th century; colleges developed in 13th–14th centuries; continuous operation. |
| University of Paris (Sorbonne) | c. 1150 (schools) / charter 1215 | France | Important medieval university; reorganized and split multiple times in modern era. |
| University of Salamanca | 1218 (charter) | Spain | Oldest in Spain; earlier roots exist; continuous operation. |
| University of Padua | 1222 | Italy | Founded by scholars from Bologna; long continuous history; early scientific reputation. |
| University of Cambridge | c. 1209 (after scholars left Oxford) | UK | Founded by dissenting scholars; continuous operation. |
| University of Montpellier | c. 1220 (medical teaching earlier) | France | Famous for its medical faculty; continuous operation. |
Case Studies: Understanding Key Institutions
While institutions such as Nalanda and Taxila are historically profound, they do not meet the continuous-operation criterion used by many “oldest university” rankings. In contrast, the likes of Bologna and Oxford do meet that condition and thus often feature in lists of “oldest universities.
1. University of al-Qarawiyyin (Fez, Morocco)
Founded in 859 CE by Fatima al-Fihri, al-Qarawiyyin began as a mosque and center for Islamic learning, and over centuries functioned as a leading madrasa. UNESCO has recognized it as the oldest existing educational institution in continuous operation. In 1965 it was incorporated into Morocco’s modern university system. Its curricula historically included theology, law, grammar, rhetoric, mathematics, astronomy and more. Because its legal university status is recent, debates persist over whether it counts as the world’s “oldest university“ in the European sense – but for broad “oldest institution” lists it is often cited first.
2. Al-Azhar University (Cairo)
The origins of al-Azhar date to around 970-972 CE under the Fatimid caliphs, with the establishment of the al-Azhar mosque and then a learning institution. Over centuries, it became one of the major centers of Sunni Islamic scholarship, jurisprudence, and theology. It now functions as a full-fledged modern university in Egypt, with faculties across social sciences, engineering, and more – illustrating how an institution with medieval roots can evolve into a modern university over more than a millennium.
3. University of Bologna (Italy)
Often cited as the oldest university in continuous operation in Europe, Bologna’s teaching community emerged around 1088 CE. It developed the legal concept of the universitas (guild of masters/students), and its alumni included many medieval jurists. Bologna remains active today, granting degrees, and its institutional identity traces through centuries. For the European university tradition, Bologna is foundational.
4. University of Oxford (UK)
Teaching at Oxford began by at least c.1096 (or shortly thereafter), with the oldest surviving colleges founded in the 13th century. Despite interruptions (e.g., plague, wars), Oxford has maintained institutional continuity. Because of its storied history and the depth of scholarship, it is always part of lists of oldest universities.
The Oldest Medical Colleges in World

Medicine has always been one of humanity’s noblest and oldest disciplines. From the early healing centers of ancient civilizations to the establishment of formal medical faculties in Europe and Asia, the journey of medical education mirrors the evolution of scientific inquiry itself. When we speak about the Oldest Medical Colleges in World, we are exploring institutions that not only pioneered modern medical teaching but also laid the foundation of today’s health-care systems, research, and clinical training.
Historical Context
For centuries, medicine was taught through apprenticeships, religious schools, or philosophical traditions. The term “medical college” came much later, as the concept of universities formalized learning in anatomy, surgery, and physiology. Ancient centers like Nalanda University (India, 5th century CE) and Gundishapur Academy (Iran, 3rd–7th century CE) served as proto-medical universities, combining studies in medicine, mathematics, and astronomy. Though they no longer exist, their intellectual legacy influenced later Islamic and European medical schools.
List of the Oldest Medical Colleges in World
| Institution | Earliest medical teaching | Region | Notes |
| Schola Medica Salernitana | 9th-10th century | Salerno, Italy | Often regarded as the first medical school in Western Europe. Integrated Greek, Arabic, and Latin medical traditions. Produced Regimen Sanitatis Salernitanum, one of the earliest medical texts. Declined in the 14th century. |
| University of Montpellier – Faculty of Medicine | 12th century (statutes 1220) | Montpellier, France | Considered the oldest continuously operating medical faculty in the world. Hosted great physicians like Nostradamus and François Rabelais. Continues as the University of Montpellier’s Faculty of Medicine. |
| University of Padua – School of Medicine | 1222 (university founded) | Padua, Italy | Founded by scholars from Bologna. Developed the first permanent anatomy theater (1594). Produced revolutionary scientists like Andreas Vesalius and William Harvey. |
| University of Bologna – Medical teaching | 11th–12th century | Bologna, Italy | One of the earliest European universities to teach anatomy and surgery. Pioneered human dissections in the 13th century; home to anatomist Mondino de’ Luzzi. |
| University of Paris – Faculty of Medicine (Sorbonne) | 12th century CE | Paris, France | Played a major role in standardizing medical education in medieval Europe. Later merged into Sorbonne University; still active. |
| University of Oxford – Medical School | 13th century CE (medical teaching since 1220s) | Oxford, England | Among the oldest medical schools in the English-speaking world. Modernized through 19th–20th century reforms; today globally top-ranked. |
| University of Cambridge – School of Clinical Medicine | c. 1318 CE (formal faculty) | Cambridge, England | Early focus on anatomy and natural philosophy. Among the world’s leading research medical schools today. |
| Charles University – Faculty of Medicine | 1348 CE | Prague, Czech Republic | One of the oldest universities in Central Europe; its medical faculty remains one of Europe’s oldest still in continuous operation. |
| University of Vienna – Faculty of Medicine | 1365 CE | Vienna, Austria | Developed the “Vienna School of Medicine,” producing significant advances in pathology and clinical diagnostics. |
| University of Heidelberg – Faculty of Medicine | 1386 CE | Heidelberg, Germany | Germany’s oldest university; its medical faculty has maintained continuous operation for over six centuries. |
| University of Copenhagen – Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences | 1479 CE | Copenhagen, Denmark | Established during the Renaissance; remains Denmark’s oldest and most prestigious medical institution. |
| University of Santo Tomas – Faculty of Medicine and Surgery | 1611 CE | Manila, Philippines | The oldest medical college in Asia still in operation; introduced Western medicine in the region; continues to train doctors today. |
| Harvard Medical School | 1782 CE | Boston, USA | Among the oldest medical schools in the United States; pivotal in shaping evidence-based and research-driven medicine. |
The Oldest Technical University in the World

Engineering and technology have shaped the modern world – from bridges and steam engines to computers and aerospace systems. The origin of formal technical education marks a turning point in human history, when scientific theory met industrial practice. When we discuss the Oldest Technical University in the World, we refer to the earliest institutions that offered organized, advanced instruction in engineering, mining, mathematics, mechanics, and applied sciences – leading to recognized academic degrees or state certifications.
Unlike medieval universities, which focused on theology, philosophy, and law, technical universities arose in response to the Industrial Revolution and state-sponsored modernization efforts. These institutions trained engineers, surveyors, and builders – the minds that powered industrial and technological revolutions across Europe and beyond.
| Institution | Year of Establishment | Country | Historical Significance & Key Facts |
| Czech Technical University in Prague (ČVUT) | 1707 | Czech Republic | Founded by Emperor Joseph I; recognized as the oldest civilian technical university in the world. Initially focused on civil engineering and surveying. Today offers 8 faculties including mechanical, electrical, and nuclear engineering. |
| École Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées (ENPC / École des Ponts ParisTech) | 1747 | France | The oldest engineering school in the world still operating. Established to train engineers for public works and infrastructure (roads, bridges, canals). Integral to France’s civil engineering heritage. |
| TU Bergakademie Freiberg | 1765 | Germany | Founded as the University of Mining and Technology. Oldest mining and metallurgy university globally. Alumni contributed to Europe’s early industrial development and geological research. |
| Budapest University of Technology and Economics (BME) | 1782 | Hungary | The world’s first institution to award engineering degrees. Played a crucial role in developing civil and mechanical engineering education in Central Europe. |
| Politecnico di Torino | 1859 | Italy | Italy’s oldest technical university; contributed to the nation’s post-unification industrial growth. Specializes in architecture, automotive engineering, and aerospace. |
| ETH Zurich (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology) | 1855 | Switzerland | Established to promote scientific and industrial progress in Switzerland. Alumni include Albert Einstein. One of the world’s top-ranked technical universities today. |
| Technische Universität Wien (TU Wien) | 1815 | Austria | Founded as the Imperial–Royal Polytechnic Institute. Pioneer in mechanical and civil engineering education in Central Europe. |
| Polytechnic University of Madrid (UPM) | 1802 (roots) | Spain | Originated as the Royal School of Civil Engineering; later merged to form Spain’s leading technical university. |
| Technical University of Braunschweig | 1745 | Germany | The oldest technical university in Germany is the Technical University of Braunschweig (TU Braunschweig), which was founded in 1745 as the Collegium Carolinum. It is a member of the TU9 Society of German Technical Universities and has a long history of excellence in engineering, natural sciences, and technology. |
| Istanbul Technical University (ITU) | 1773 | Turkey | Began as the Imperial School of Naval Engineering under Ottoman rule. Recognized by UNESCO as one of the oldest technical universities. |
| Saint Petersburg State Mining University | 1773 | Russia | Russia’s oldest engineering higher education institution, established by Empress Catherine the Great to train mining engineers. |
| Technische Universität Berlin (TU Berlin) | 1770 (roots) | Germany | One of the first German polytechnic schools; later became TU Berlin. Contributed significantly to Germany’s industrial and architectural innovation. |
| Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) | 1861 | USA | Founded during the American Industrial Revolution; became the global model for combining research and engineering education. |
| Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee (formerly Thomason College of Civil Engineering) | 1847 | India | Asia’s oldest technical institution; trained engineers for canal and railway projects during British India; later became IIT Roorkee in 2001. |
Why these institutions matter: Legacy & modern relevance
The significance of tracking the Oldest Universities in the World is more than trivia – these institutions embody many of the enduring features of higher education:
- They established the degree structure (bachelor, master, doctorate) and academic hierarchies, particularly in the European tradition (Bologna, Paris, Oxford).
- They were centres of knowledge transmission across cultures. For example, al-Qarawiyyin and al-Azhar preserved and built upon Arabic, Islamic and Mediterranean scholarship; Salerno and Montpellier integrated Arabic medical texts into European medicine.
- They pioneered professional education in law, medicine, engineering – hence the relevance of the oldest medical colleges and earliest technical universities.
- Many have global reputations and continue to attract students, scholars and research funding, thereby connecting past legacies with modern educational systems.
- They remind us that continuity matters: a university is more than a building or name – it is the layered tradition of teaching, scholarship, institutional memory, and degrees.
Therefore, whichever definition one uses, listing the Oldest Universities in the World gives insight into how higher education developed globally.
Timeline of the Oldest Universities
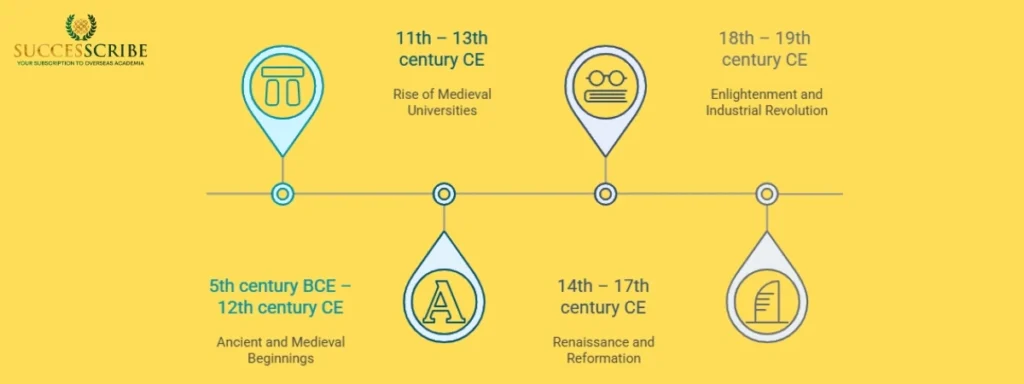
| Period | Key Institution Founded | Region |
| 5th century BCE – 12th century CE | Taxila, Nalanda, al-Qarawiyyin, Al-Azhar | South Asia & North Africa |
| 11th – 13th century CE | Bologna, Oxford, Paris, Salamanca, Padua | Western Europe |
| 14th – 17th century CE | Charles University, Vienna, Heidelberg, Santo Tomas | Central Europe & Asia |
| 18th – 19th century CE | ČVUT, École des Ponts, TU Freiberg, IIT Roorkee | Modern Technical Universities |
Evolution of the Oldest Universities in the World: Challenges and Triumphs
The oldest universities in the world face 21st-century hurdles: funding cuts (e.g., Bologna’s 10% state reduction in 2024), digital divides, and inclusivity gaps. Yet, triumphs abound – Oxford’s net-zero pledge by 2035 invests £1 billion in green tech, while Al-Azhar’s online fatwa platform reaches 50 million users monthly.
Post-2020, hybrid models boosted enrollment by 12% across these sites, per OECD data. They contribute $500 billion globally in IP value, with Cambridge’s Silicon Fen spawning 5,000 startups since 1985.
| Challenge | Impact on Oldest Universities | Response |
| Funding | 15% EU cuts post-Brexit | Bologna: €200M private partnerships |
| Diversity | 20% female STEM gap | Padua: 50% target by 2030 |
| Tech Integration | AI ethics debates | Al-Azhar: Dedicated faculty |
| Climate | Campus emissions up 8% | Oxford: Carbon-neutral labs |
This table illustrates proactive strategies, ensuring longevity.
Conclusion
The quest to identify the Oldest Universities in the World demonstrates both the endurance of scholarship and the evolution of institutional forms. Whether one starts with al-Qarawiyyin (859) or Bologna (1088) depends on one’s criteria, but the broader truth remains: higher education has roots stretching deep into the past, across continents, in many traditions.
We also see that specialized branches – such as the oldest medical colleges in world (e.g., Montpellier, Salerno) and the oldest technical university in the world (e.g., ČVUT, École des Ponts) – reflect how academic institutions diversified and adapted.
FAQs
Which is the single oldest university in the world?
It depends on the criterion. If you count the earliest founded institution of higher learning still extant, al-Qarawiyyin (859) is often named. If you require the medieval European universitas model and continuous degree-granting identity, University of Bologna (c. 1088) is the usual answer. Both claims have scholarly support; the difference is definitional.
Is Nalanda older than Bologna?
Yes – Nalanda dates to the 5th century CE – but it was destroyed in the 12th century and thus does not have continuous operation into the modern era, so it’s treated differently in “oldest university” lists.
What are the oldest medical and technical schools?
Medical – Schola Medica Salernitana (9th–10th c.) and the Faculty of Medicine at Montpellier (continuous from 12th c.) are key early centers. Technical – depending on definition: Czech Technical University (1707) has earlier roots for engineering education; École des Ponts (1747) is the oldest formal civil engineering school; TU Freiberg (1765) is the oldest mining university.
Which Asian university is the oldest still functioning today?
The University of Santo Tomas (1611) in the Philippines is Asia’s oldest existing university and medical college still in operation.
Do any of the ancient universities still hold religious affiliations?
Yes. Al-Azhar University in Cairo remains a leading center of Islamic theology, while maintaining faculties in science, engineering, and medicine.
Related Post
Toughest exams in the world
Hardest degrees in the world
Highest paying jobs in Austria
Highest paying jobs in USA















